Hot Topics
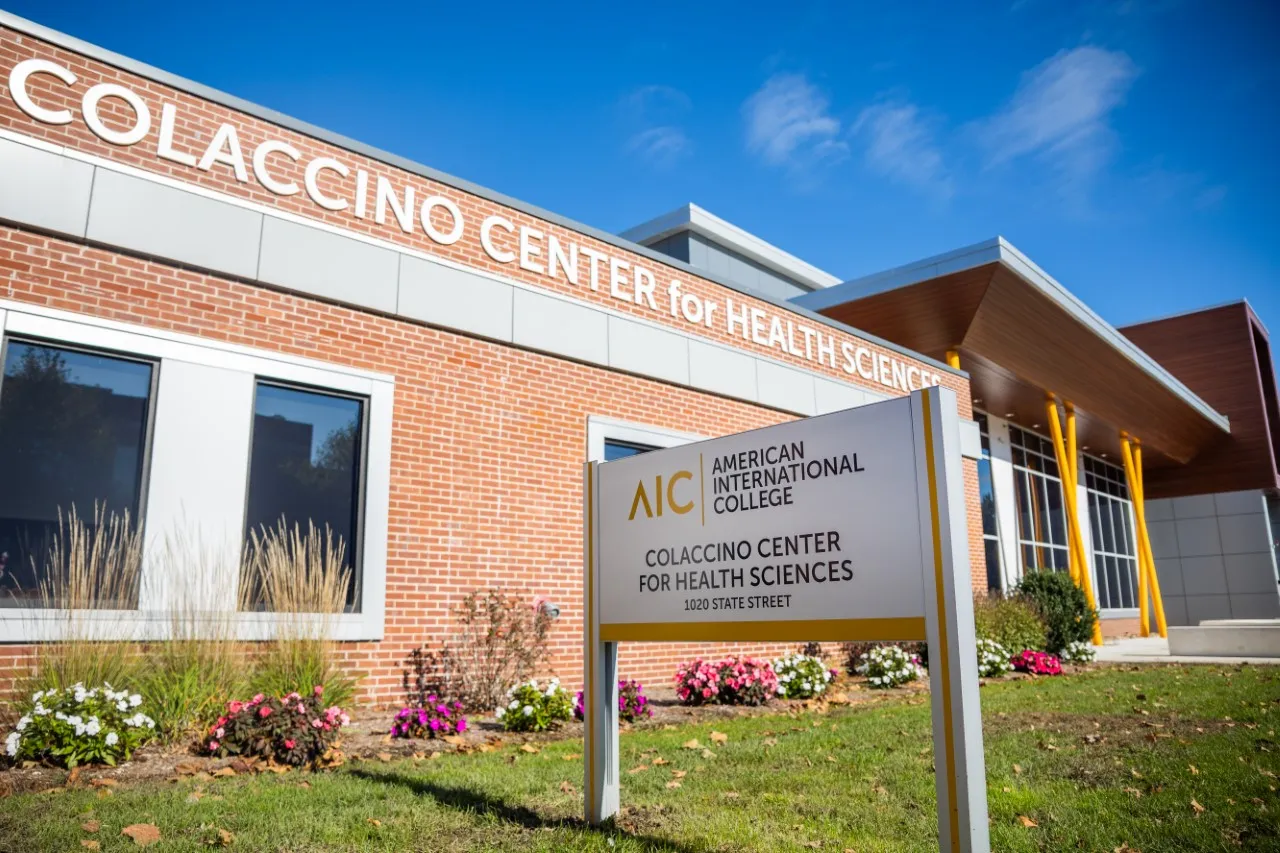
10 Reasons to Attend American International College (aic.edu)
Here are 10 reasons to attend American International. To find out more information about the…
Latest Informational Posts
Latest
What Is Blog SnapSourceNet? Everything You Need To Know
Navigating the demands of creating compelling blog content in today’s digital landscape can often seem daunting. However, a revolutionary solution…
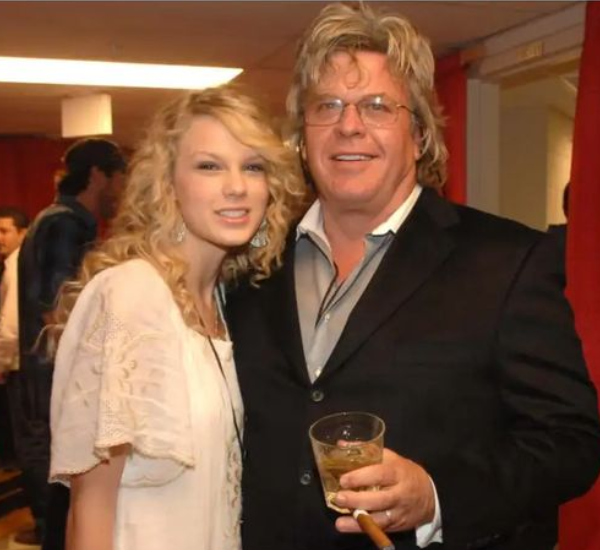
Who Is Lori Brice?Know All About Ron White’s Ex-Wife
Lori Brice gained recognition through her marriage to renowned stand-up comedian Ron White, known for his contributions to the Blue…
Pink:gdxr6qp7qy0= Wallpaper: 10 Eco-Friendly Design Ideas for Your Home
Step into a welcoming ambiance where every corner radiates joy from the moment you enter. Join us as we delve…
Design:5exwzo_yaxi= Background: Crafting Engaging Digital Interfaces
In the world of digital design, the design:5exwzo_yaxi= background plays an integral role in shaping both user experience and visual…
What Is www FameBlogsNet? Main Moto Of Their Blogs
The Evolution Of www FameBlogsNet Awaits You, Ready? An extensive analysis of the newest features on www. At fameblogs, creativity…